이것이 자바다 의 Chapter08 을 참고하여 정리한 포스트입니다.
Chapter 08. 인터페이스 - (6)
7. 디폴트 메소드와 인터페이스 확장
디폴트 메소드 : 인터페이스에 선언된 인스턴스 메소드이므로 구현 객체가 있어야 사용 가능하다.
- 선언은 인터페이스, 사용은 구현 객체를 통해 한다.
7.1 디폴트 메소드의 필요성
인터페이스에서 디폴트 메소드를 허용한 이유
- 기존 인터페이스를 확장해서 새로운 기능을 추가하기 위해서다
- 기존 인터페이스의 이름과 추상 메소드 변경 없이 디폴트 메소드만 추가 가능함
- 윗 줄의 이유로 이전에 개발한 구현 클래스를 그대로 사용하면서 새롭게 개발하는 클래스로 디폴트 메소드를 활용 가능
ex) 디폴트 메소드가 필요한 경우
- 기존 MyInterface 인터페이스
- 이를 구현한 MyClassA 클래스의 method1() 메소드
-
위의 구성에서 기능을 추가하려고 MyInterface 에 추상 메소드를 추가하면 MyClassA에서 문제가 발생한다.
- 예시 오류 이유
- 추가된 추상 메소드에 대한 실체 메소드가 MyClassA 에 없기 때문이다.
- 디폴트 메소드 추가로 오류 해결
- MyInterface 에 디폴트 메소드를 선언한다.
- 디폴트 메소드는 추상 메소드가 아니기 때문에 구현 클래스에서 실체 메소드를 작성할 필요가 없다. (MyClassA 사용 가능)
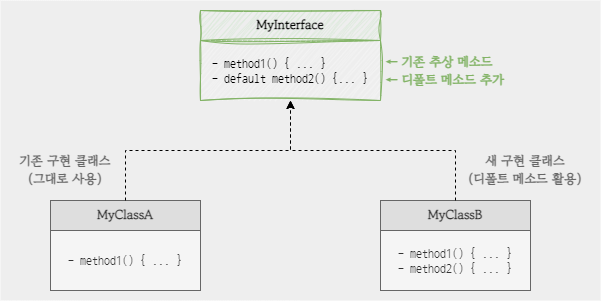
- 수정한 MyInterface 를 구현한 새로운 MyClassB 구현 클래스는 method1() 내용은 반드시 채워야 한다.
- MyClassB 구현 클래스에서 디폴트 메소드인 method1() 는 MyInterface 에 정의된 것을 사용하거나 재정의해서 사용할 수 있다.
MyInterface.java기존 인터페이스1 2 3
public interface MyInterface { public void method1(); }
MyClassA.java기존 구현 클래스1 2 3 4 5 6
public class MyClassA implements MyInterface { @Override public void method1() { System.out.println("MyClassA-method1() 실행"); } }
MyInterface.java수정 인터페이스1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
public interface MyInterface { public void method1(); // 디폴트 메소드 추가 public default void method1() { System.out.println("MyInterface-method2() 실행"); } }
인터페이스를 수정해도 MyClassA 는 컴파일 에러가 발생하지 않는다.
MyClassB새로운 구현 클래스1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
public class MyClassB implement MyInterface { @Override public void method1() { System.out.println("MyClassB-method1() 실행"); } //디폴트 메소드 재정의 @Override public void method2() { System.out.println("MyClassB-method2() 실행"); } }
DefaultMethodExample.java디폴트 메소드 사용1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
public class DefaultMethodExample { public static void main(String[] args) { MyInterface mi1 = new MyClassA(); mi1.method1(); mi1.method2(); MyInterface mi2 = new MyClassB(); mi2.method1(); mi2.method2(); } }
실행결과 MyClass-method1() 실행
MyInterface-method2() 실행
MyClassB-method1() 실행
MyClassB-method2() 실행- MyClassA 의 method2() 는 MyInterface 에 정의된 디폴트 메소드가 실행되었다.
7.1 디폴트 메소드가 있는 인터페이스 상속
부모 인터페이스에 디폴트 메소드가 정의되어 있을 때 자식 인터페이스에서 디폴트 메소드 활용 방법
- 디폴트 메소드를 단순히 상속만 받는다.
- 디폴트 메소드를 재정의(Overrid) 해서 실행 내용을 변경한다.
- 디폴트 메소드를 추상 메소드로 재선언한다.
ex) 인터페이스 메소드 호출
추상 메소드와 디폴트 메소드가 선언된 ParentInterface 와 자식 인터페이스들이 구성된다고 가정한다.
ParentInterface.java부모 인터페이스1 2 3 4 5 6
public interface ParentInterface { public void method1(); public default void method2() { System.out.println("ParentInterface-method2 실행"); } }
ChildInterface1.java자식 인터페이스1 2 3 4
public interface ChildInterface1 extends ParentInterface { //자식 인터페이스의 추상 메소드 method3() 선언 public void method3(); }
이럴 경우 ChildInterface 인터페이스를 구현하는 클래스는 method1()과 method3() 의 실체 메소드를 가지고 있어야 한다.
ParentInterface 의 method2() 를 호출할 수 있다.Implementation1.java구현 클래스1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21
public class Implementation1 { public static void main(String[] args) { ChildInterface1 ci1 = new ChildInterface1() { @Override public void method1() { System.out.println("Implementation1-method1 실행"); } @Override public void method3() { System.out.println("Implementation1-method3 실행"); } }; ci1.method1(); ci1.method2(); //ParentInterface 의 method2() 호출 ci1.method3(); } }
실행 결과 Implementation1-method1 실행
ParentInterface-method2 실행
Implementation1-method3 실행
ChildInterface2.java자식 인터페이스1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
public interface ChildInterface2 extends ParentInterface { @Override //디폴트 메소드 method2() 재정의 public default void method2() { System.out.println("ChildInterface2-method2 실행"); } //자신의 추상 메소드로 선언 public void method3(); }
이 경우도 ChildInterface2 인터페이스를 구현하는 클래스는 method1(), method3() 의 실체 메소드를 가져야 한다.
ChildInterface2 에서 재정의한 method2() 를 호출할 수 있다.Implementation2.java구현 클래스1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20
public class Implementation2 { public static void main(String[] args) { ChildInterface2 ci2 = new ChildInterface2() { @Override public void method1() { System.out.println("Implementation2-method1 실행"); } @Override public void method3() { System.out.println("Implementation2-method3 실행"); } }; ci2.method1(); ci2.method2(); //ChildInterface2 의 method2() 호출 ci2.method3(); } }
실행결과 Implementation2-method1 실행
ChildInterface2-method2 실행
Implementation2-method3 실행
ChildInterface3.java자식 인터페이스1 2 3 4 5 6 7
public interface ChildInterface3 extends ParentInterface { @Override //디폴트 메소드 method2() 를 추상 메소드로 재선언 public void method2(); //자신의 추상 메소드로 선언 public void method3(); }
이 경우에는 ChildInterface3 인터페이스를 구현 클래스는 method1(), method2(), method3() 의 실체 메소드를 모두 가지고 있어야 한다.
-
Implementation3.java구현 클래스1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25
//ChildInterface3 인터페이스 구현 클래스 public class Implementation { public static void main(String[] args) { ChildInterface3 ci3 = new ChildInterface3() { @Override public void method1() { System.out.println("Implementation3-method1 실행"); } @Override public void method2() { System.out.println("Implementation3-method2 실행"); } @Override public void method3() { System.out.println("Implementation3-method3 실행"); } }; ci3.method1(); ci3.method2(); //ChildInterface3 구현 객체의 method2() 호출 ci3.method3(); } }
실행결과 Implementation3-method1 실행
Implementation3-method2 실행
Implementation3-method3 실행
🌞 정보 : 공부 기록용 블로그입니다. 오타나 내용 오류가 있을 경우 알려주시면 감사하겠습니다.

댓글남기기